Self Declaration reception process

|
Project:
|
Self Declaration reception process : FRAME_Diagram diagram
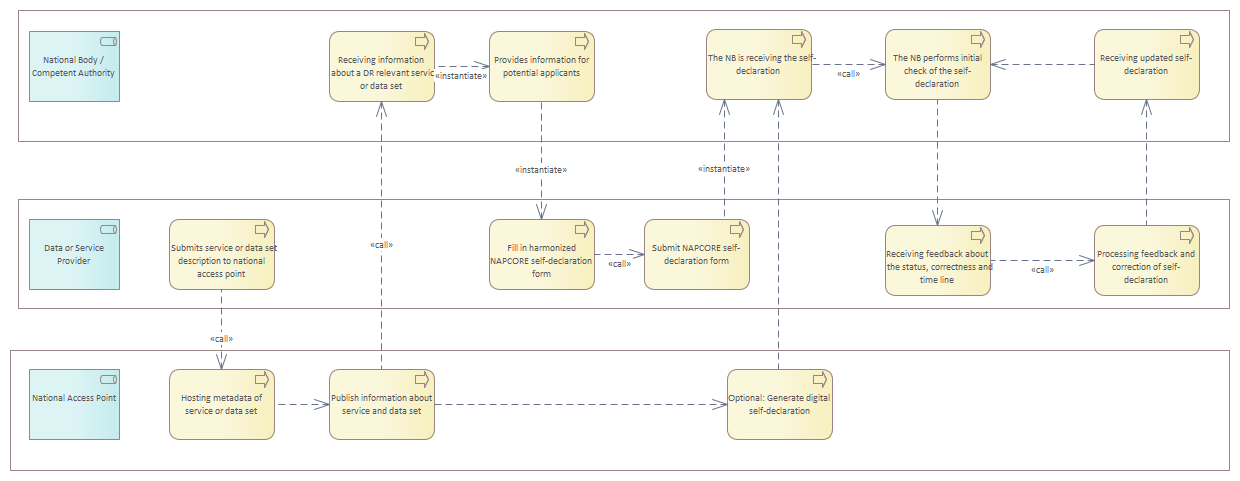
Member State shall designate an impartial and independent National Body and make sure that this National Body is properly authorised, according to national regulations, to receive and process self-declarations. The National Body will need the following preparation before being ready to receive self-declarations:<br/>Identify and organise resources for receiving and processing self-declarations and for performing compliance assessment and random inspections.<br/>Develop an internal process for receiving and processing self-declarations, taking into account both European regulation and contextual factors present in the Member State such as the number of service or data providers expected to submit a self-declaration and national administrative law.<br/>Develop a plan on how to identify data and service providers covered by the delegated regulation and how the National Body will approach the stakeholders. Provide national templates for self-declarations and accompanying documents.·Compile Member State specific instructions for data and service providers on how to fill in and submit a self-declaration and related accompanying documents. After the National Body has been nominated and necessary preparations have been carried out, it will provide information to potential data and service providers on their obligation to submit a self-declaration and provide instructions on how to fill in and submit a self-declaration. The National Body may inform the stakeholders with different methods such as email campaigns, sending letters, publishing information on the NAP website or arranging workshops. To identify the relevant actors obligated to submit a self-declaration, the National Body may use procedures specific to its Member State. These may include e.g. utilization of the contacts of the NAP operator. Good knowledge of the national mobility landscape is required to identify the stakeholders potentially having an obligation to submit a self-declaration. To increase its knowledge and to build a more complete picture of the mobility landscape, the National Body may collaborate with local or regional transport authorities. When exchanging information between authorities, GDPR compliance is necessary. After being contacted by the National Body, the data or service provider submits a data set or service to the National Access Point (NAP), international access point or content access point as required by the applicable delegated regulation. After submitting the service or data set, the provider fills in and submits the self-declaration form to the National Body. This can take place either electronically (i.e., by email or by indicating compliance via a checkbox) or in paper form. The processing of a self-declaration form starts with verification of the contact details of the data or service provider and checking whether the National Body is responsible and acknowledged for the respective delegated regulation.<br/>In case of incomplete or inconsistent contact details, the National Body may request the data or service provider to update its contact details. If the stakeholder does not provide the missing contact details or does not correct erroneous contact details, the National Body may stop processing the self-declaration. After verification of contact details, the National Body verifies the completeness of the self-declaration. In practice, this means checking that all mandatory fields of the self-declaration form have been filled in, and all required accompanying documents have been provided. If needed, the National Body may request the data or service provider to update the self-declaration and complete the missing parts. After a complete self-declaration has been received, the National Body can provide an acknowledgement to the data or service provider. After receiving and processing the self-declaration, the National Body might update the results to a registry/database (which is not compulsory) of processed self-declarations. At the same time, the National Body may also update the registry of compliant services and data sets (optional), if it has been established in the Member State. Contents of these registries will be the basis for periodic reporting related to the ITS Directive and delegated regulations in the Member State and at the European level. The random inspections that are carried out periodically at pre-determined intervals also check the collected self-declarations and descriptions of compliant services and data sets. In the following figures, digital map producers and broadcasters are included in data or service provider<br/><br/>
|

